|
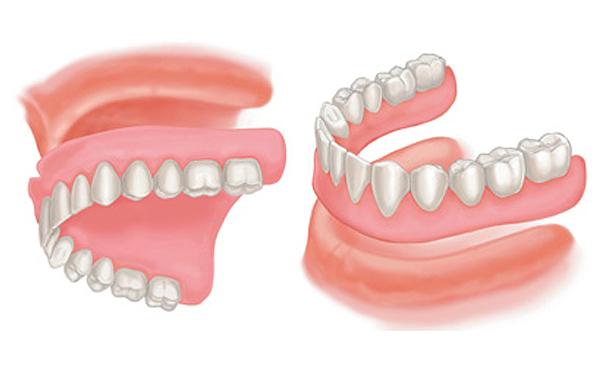
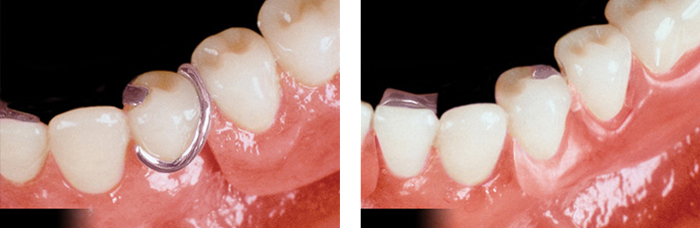
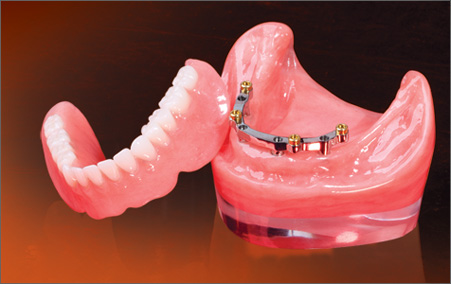
Complete dentures Complete dentures can be either “conventional” or “immediate”. Made after the teeth have been removed and the gum tissue has begun to heal, a conventional denture is ready for placement in the mouth about eight to 12 weeks after the teeth have been removed. Unlike conventional dentures, immediate dentures are made in advance and can be positioned as soon as the teeth are removed. As a result, the wearer does not have to be without teeth during the healing period. However, bones and gums shrink over time, especially during the healing period following tooth removal. Therefore a disadvantage of immediate dentures compared with conventional dentures is that they require more adjustments to fit properly during the healing process and generally should only be considered a temporary solution until conventional dentures can be made. A removable partial denture or bridge usually consists of replacement teeth attached to a pink or gum-colored plastic base, which is connected by metal framework that holds the denture in place in the mouth. Partial dentures are used when one or more natural teeth remain in the upper or lower jaw. A fixed (permanent) bridge replaces one or more teeth by placing crowns on the teeth on either side of the space and attaching artificial teeth to them. This “bridge” is then cemented into place. Not only does a partial denture fill in the spaces created by missing teeth, it prevents other teeth from changing position. A precision partial denture is removable and has internal attachments rather than clasps that attach to the adjacent crowns. This is a more natural-looking appliance. Over Dentures Over dentures are a series of mini-implants which stabilize dentures. With mini-implants, patients can “snap” the dentures in place for a more secure fit and confident denture experience. Alternatives to dentures Yes, dental implants can be used to support permanently cemented bridges, eliminating the need for a denture. The cost is usually greater, but the implants and bridges more closely resemble the feel of real teeth. Dental implants are becoming the alternative to dentures but not everyone is a candidate for implants. We will be happy to schedule a consultation appointment to discuss if you are a candidate for dental implants. Does insurance cover the cost of dentures? Most dental insurance providers cover some of the cost of dentures. However, contact your company to find out the specifics of what they will cover. How are dentures made? The denture development process takes about three to six weeks and several appointments. Once we determine what type of appliance is best for you, the general steps are to:
What do new dentures feel like? New dentures may feel a little odd or loose for a few weeks until the muscles of the cheeks and tongue learn to keep them in place and you get comfortable inserting and removing them. Also, it is not unusual for minor irritation or soreness to occur and for saliva flow to increase when you first start wearing dentures, but these problems will diminish as the mouth adjusts. How dentures look Dentures are made to closely resemble your natural teeth so there should be no noticeable change in appearance. In fact, dentures may even improve your smile and fill out your facial appearance. Eating with dentures Eating with new dentures will take a little practice and may be uncomfortable for some wearers for a few weeks. To get used to the new denture, start with soft foods cut into small pieces. Chew slowly using both sides of your mouth. As you get used to new dentures, add other foods until you return to a normal diet. Be cautious with hot or hard foods and sharp-edged bones or shells. And, avoid foods that are extremely sticky or hard. You may want to avoid chewing gum while you adjust to the denture. Also, don’t use toothpicks while wearing dentures. Will dentures change how I speak? After getting dentures, you may have difficulty pronouncing certain words. If so, practice by saying the difficult words out loud. With practice and with time you will become accustomed to speaking properly with dentures. Dentures may occasionally slip when you laugh, cough, or smile. Reposition the dentures by gently biting down and swallowing. During the first several days after receiving your denture, you may be asked to wear it all the time, including while you sleep. Although this may be temporarily uncomfortable, it is the quickest way to identify the areas on the denture that may need adjustment. Once adjustments are made, you should remove dentures before going to bed. This allows gum tissues to rest and allows normal stimulation and cleansing by the tongue and saliva. The denture can be put back in the mouth in the morning. Should I use a denture adhesive? A denture adhesive may be considered under the following circumstances:
When shouldn’t denture adhesives be considered? There are situations when denture adhesives should not be used. Those cases include:
How are denture adhesives applied? Here are some tips to consider when applying denture adhesives:
Types of denture adhesives
Are adhesives safe? Dental adhesives are safe as long as they are used as directed. If the denture is well-fitting and the adhesive is only used to give added stability, there should be no ill effects. If adhesives are used excessively to fill voids for an ill-fitting denture, they can be harmful to the underlying soft and hard tissues. Occasionally, in these cases, inflammation of the soft tissues can result. In addition, because of its movement on the soft tissue and underlying bone, an ill-fitting denture can cause bone loss. |
||||
|
|